Many women seek non-hormonal, device-free ways to prevent pregnancy (Natural Birth control Methods)—whether to avoid side effects, honor their body’s natural rhythms, or align with personal or cultural beliefs. Natural contraception methods, also called fertility awareness-based methods (FAMs), rely on observing cycle cues or behavioral strategies to estimate fertile windows. While appealing for being “natural,” these methods carry higher failure rates than hormonal or barrier options and offer no protection against sexually transmitted infections. A clear understanding, disciplined tracking, and often professional guidance are essential before relying solely on them.
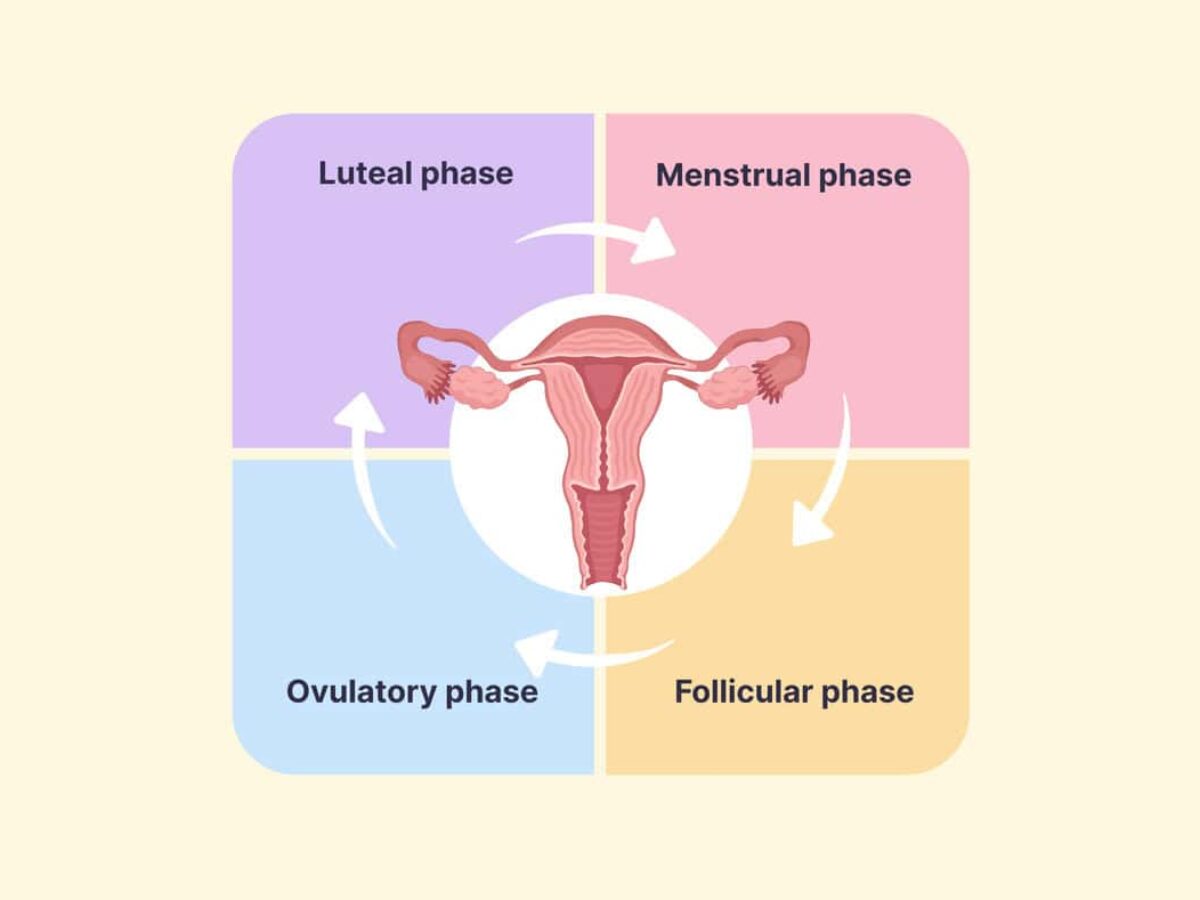
1. Calendar (Rhythm) Method
How It Works
Track your menstrual cycle lengths over several months to predict your fertile window and avoid unprotected intercourse during those days.
Advantages
-
No tools or medications needed
-
Simple and cost-effective
Disadvantages & Risks
-
Only reliable for women with very regular cycles
-
Ovulation timing can shift unpredictably
-
Typical-use failure rate up to 24% per year
2. Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Method
How It Works
Measure your resting (basal) body temperature every morning before getting out of bed. A small temperature rise signals that ovulation has just occurred.
Advantages
-
Enhances personal understanding of one’s cycle
-
Requires only a thermometer and chart
Disadvantages & Risks
-
Must be taken at the same time daily under consistent conditions
-
Illness, stress, lack of sleep, or alcohol can skew readings
-
Typical-use effectiveness between 76% and 91%
3. Cervical Mucus (Billings) Method
How It Works
Observe changes in cervical mucus throughout your cycle. Clear, stretchy, egg-white–like mucus indicates peak fertility.
Advantages
-
No external tools required
-
Fosters deeper awareness of menstrual health
Disadvantages & Risks
-
Requires careful, daily mucus checks
-
Can be unreliable during infections or hormonal fluctuations
-
Typical-use failure rates similar to other single-indicator methods
4. Symptothermal Method
How It Works
Combine BBT tracking, cervical mucus observation, and sometimes cervical position checks to more precisely identify fertile days.
Advantages
-
Higher accuracy, with up to 98% effectiveness when perfectly followed
-
Multiple data points reduce misinterpretation
Disadvantages & Risks
-
Very demanding: several observations per day, charting, and possible professional instruction
-
Stress, travel, illness, or skipped observations decrease reliability
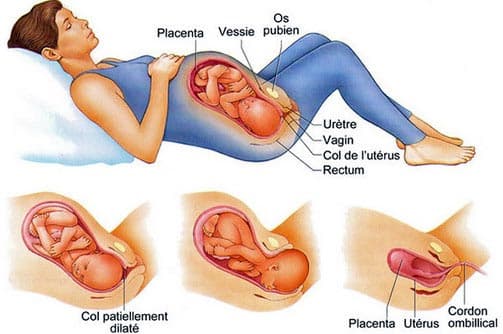
5. Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM)
How It Works
Exclusive, on-demand breastfeeding can suppress ovulation for up to six months postpartum—provided the baby isn’t given supplements or solid foods.
Advantages
-
Over 98% effective in the first six months when strictly practiced
-
No additional devices or hormones needed
Disadvantages & Risks
-
Effectiveness wanes as feeding frequency decreases or complementary feeding begins
-
Requires transition to another method once criteria are no longer met
6. Withdrawal (Coitus Interruptus)
How It Works
The male partner withdraws the penis before ejaculation to prevent sperm from entering the vagina.
Advantages
-
No devices, medications, or charts required
-
Immediately available, cost-free
Disadvantages & Risks
-
Depends entirely on partner’s self-control and timing
-
Pre-ejaculatory fluid can contain sperm
-
Typical-use failure rate around 22% per year
Which Natural Method Is Right for You?
Natural methods demand rigorous daily commitment and clear, consistent cycle patterns. They do not protect against STIs, so combining them with barrier methods (e.g., condoms) may be wise. Women with irregular cycles, partners who may struggle with timing, or anyone unable to monitor their bodies daily should consider alternative or backup methods. Consulting a healthcare provider or a certified fertility-awareness educator can help ensure correct application and maximize effectiveness.